For a few weeks now, we are working on several internal projects. We are currently developing different products and services, which we want to release soon™️. We started from scratch, so we had the freedom to choose our tools, technologies and frameworks. We decided to deploy our application on a Kubernetes cluster on the Google Cloud. Here is a short howto, to automate the deployment process.
Getting started

First, we need an account on Google Cloud. When you register for the first time, they give you access to the clusters and $300 in credit.
- Google Cloud account is required
- Node.js (v10.x)
- npm (v5.6.0)
- Docker
- Git & GitLab
We are using the GitLab AutoDeploy, Google Cloud, Vue.js and Docker to build this CI/CD.
Creating The Vue App
# let's create our workspace
mkdir vue-ci-app
cd vue-ci-app/
# install vue
npm install @vue/cli -g
# create the vue-app (select default settings)
vue create vue-app
cd vue-app/
# let's test out the app locally
npm run serve
We first create a folder and enter it, then we use
Docker Config
FROM node:lts-alpine
# install simple http server for serving static content
RUN npm install -g http-server
# make the 'app' folder the current working directory
WORKDIR /app
# copy both 'package.json' and 'package-lock.json' (if available)
COPY package*.json ./
# install project dependencies
RUN npm install
# copy project files and folders to the current working directory (i.e. 'app' folder)
COPY . .
# build app for production with minification
RUN npm run build
EXPOSE 5000
CMD [ "http-server", "-p 5000", "dist" ]
- From pulls the latest node from the public docker registry (Docker Hub)
- Then we install
http -server, a simple static serve - Afterwards, we make a directory where we will place the app
- Copy our package.json local machine to the docker instance
- After installing the dependencies and copying the dist of the app, we run a build which we serve using
http -server - This is all done in a docker container
GitLab & Kubernetes

The last part of the deployment begins with setting up a Kubernetes cluster and enabling GitLab Autodeploy.
First, we need to go to our Project > Settings > CI/CD > Auto DevOps. Enable the default pipeline. This is the auto part that escapes the need for
Then we need to add a cluster which means going to our GC account and setting up a Kubernetes cluster. We need to specify a name, environment scope, type of project, region, number of nodes, machine type, and whether it’s an RBAC-enabled cluster.
We need to go to GitLab, to the CI/CD page, and add a GitLab runner, this needs to be configured to run
We need to set a base domain, and finally add our created Kubernetes cluster to the GitLab Autodeploy.
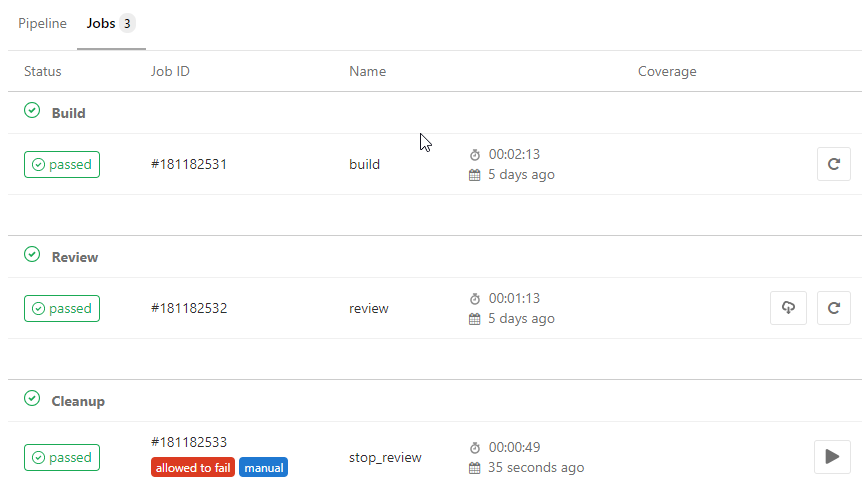
We have three jobs if all is set up and done, build and review phases where we have a build on the remote Kubernetes cluster and review where we can add linting and tests. Cleanup is a manual job that deletes the commit from the pipeline ready to be deployed again.




